Go Green with Low-E Insulation
All insulation is designed for environmental control and to reduce life cycle running costs. A lot of companies claim their insulation is eco friendly insulation simply because it is an insulation material. Not a lot of companies explain how their product is made or calculate the carbon cost of their production….. but we have.
Common Questions On Low-E Environmental Credentials
We get ask a lot questions about Low-E Insulation and its environmental credentials. So this blog has been put together to answer some of our most FAQs.
- What is the recycled material in Low-E Insulation?
- What is Low-E Insulations GWP?
- What are the environmental benefits of using Low-E Insulation?
- What about the cost of transporting Low-E by sea?
- How have you calculated the carbon footprint of Low-E Insulation?
- Is any insulation Carbon Negative?
What is the Recycled Material in Low-E Insulation?
Low-E Insulation is manufactured from non-toxic, recycled, closed cell polyethylene foam which is made from recycled milk cartons. For the last 10 year we have manufactured our products using up to 40% recycled material. More recently we have managed to increase our recycled content up to 80%. And one day soon we hope to make the core of our products 100% recycled material.
Not only does this reduce the need for refining and processing of raw materials, it also helps to keep a mass-use single product from reaching landfill (or our oceans). The recycled content can affect the colour, but not the quality or thermal properties, of our foam. Our foam can be anything from white to green, or even brown.

What is Low-E Insulations GWP?
Low-E Insulation has ZERO Global Warm Potential (GWP). However, nearly all insulation materials can make claims of zero GWP because they insulate and reduce CO2 during their life cycle.
Low-E Insulation has one of the lowest Carbon Footprints of any Insulation product manufactured today, even without considering its life-cycle use. This is due in no small part to our patented production method which eliminates the use of glues, adhesives, and solvents. Once our life cycle cost are taken into account Low-E Insulation actually has a Carbon Negative Footprint.

What are the Environmental Benefits of Using Low-E Insulation?
Recycled Material
Our closed cell, non-toxic, core is manufactured from recycled pre and post-consumer goods. This has three advantages for the environment: It uses less natural resources, It diverts materials from the solid waste stream, It uses less energy during manufacturing.
Innovative Design
Low-E Insulation is an air-infiltration and vapour barrier with sound deadening qualities and thermal control all-in-one. Low-E Insulation tackles all 3 forms of heat loss, provides moisture control and reduces draughts and air leakage.
Efficiency
It is one of the most efficient Insulations on the market and using Low-E is guaranteed to reduce energy bills and life cycle costs.
“People don’t understand, it doesn’t just save space in a building. Utilising Low-E Insulation allows us to design thinner wall and roof profiles. This means we can use smaller timbers, shorter nails and screws and leave more internal floor space., but the benefits don’t stop there. It also means less material brought to site, less vehicles on our road and less material to handle and install, making the build process quicker and easier. We produce less waste on site and have less waste to transport to landfill. The knock-on effects of utilising Low-E in a building are huge.”
– Anthony Brown, Director at Dwell Design Architects
Reducing CO2 Output
Low-E Insulation can be installed in walls, lofts and many more DIY applications and can assist you and your building in increasing efficiency while lowering CO2 output.
Air Infiltration
This reduces gaps and air leakage. According to new UK and European research, air leakage can account for up to 50% of energy consumed in a building.
Moisture Control
The unique design of Low-E Insulation means it will not absorb moisture and does not promote mould or fungus growth. This means it can be used to improve the performance of other insulations when used in combination systems.

Air Quality
Unlike other insulation materials, Low-E does not ‘off’ gas which can negatively affect air quality. This non-itchy, fibre free insulation medium is completely safe to handle and install.
Eco Friendly
While there are many types of eco-friendly insulation, Low-E is manufactured using a patented process, there are no glues or adhesives used which could break down over time resulting in short life expectancy of the product or which might fuel a fire.
Space Saving
Low-E will add higher thermal efficiency without occupying increased space. Incorporating Low-E Insulation in any insulation system means the profile of the system can be made smaller/narrower.
Ancillary Costs
This also reduces the thickness of ancillary components such as steels, timbers, secondary insulation, nails, screws or other fixings. Reducing ancillary components reduces haulage and takes trucks off the road. It also has the added benefit of reducing internal/occupied space and reducing overall costs.
Packaging and Waste Management
Our large compact rolls also require less packaging and produce less waste. As well as being more economical, this has a massive benefit on the environment.
Transport
Low-E Insulation can be transported with up to 8 times more M² per load. Saving fuel and reducing the number of carbon miles on the product.
End of Life
Low-E Insulation is designed to last as long as the insulation system it is contained within. But the aluminium and the polyethylene foam are both 100% recyclable.
What about the cost of transporting Low-E by sea?
Sea Freight
We often get asked about the carbon cost of the sea transportation of Low-E Insulation. In fact, this has little impact on our Carbon Footprint.
Shipping goods by Sea Freight is very efficient and it is becoming more efficient and has less of an environmental cost as more and more companies moved towards greener bio diesels fuels for Sea Freight.
We fit over 9,000 m2 of Low-E Insulation into a standard shipping container. To put the into context, a well packed lorry full of PIR foam only holds approx. 500 m2 of material.
How Have You Calculated the Carbon Footprint of Low-E Insulation?
Independently assessed
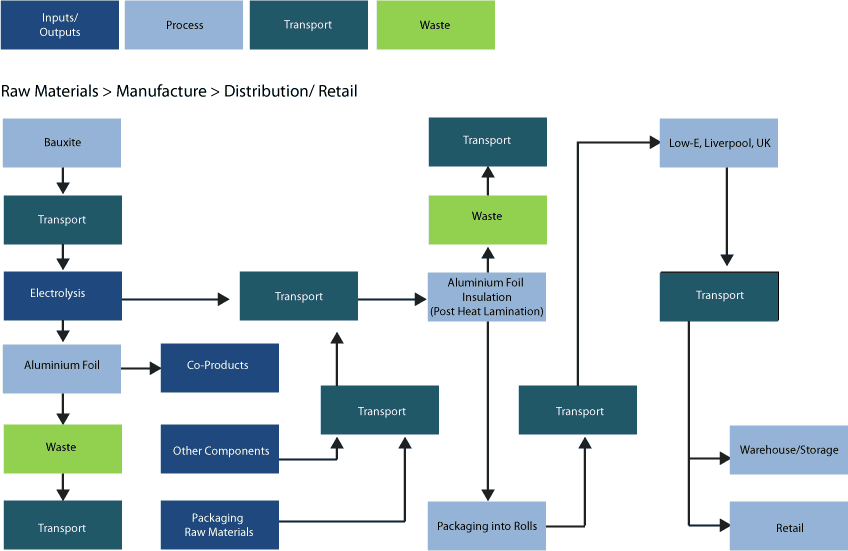
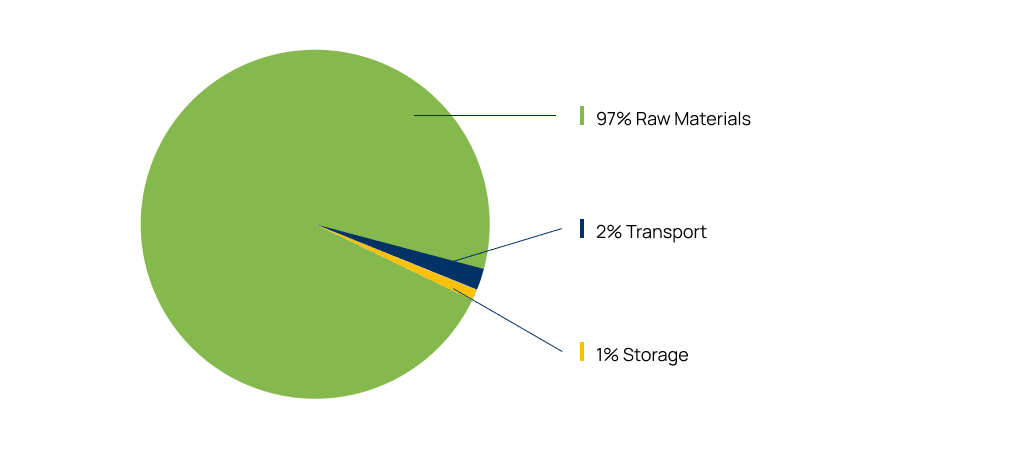
We took a great deal of time and worked very closely with C-Tech Innovation to have the carbon footprint of Low-E Insulation independently tracked. C-Tech calculated our Carbon Footprint working from our raw materials, all the way through to production and distribution.
These findings (right) are calculated by C-Tech Innovations using the recognised CCalC (Carbon Calculations over the Life Cycle) tool.
The unique design of Low-E Insulation and the fact that no glues, adhesives, or solvents are used during production gives Low-E Insulation one of the lowest Carbon Footprints of any insulation product on the market today. Our Large compact rolls add little in the way of Carbon Miles
The Carbon Footprint of Low-E Insulation at distribution is approx. 37g of Co2 per m2.

Is any insulation Carbon Negative?
Carbon Negative Products
A lot of insulation materials will claim that they are carbon negative simply because the insulate and therefore reduce carbon emissions. However, those claims often do not consider the supply chain, the manufacturing process or the product itself.
Low-E Insulation has one of the lowest carbon footprints of any insulation material on sale today. As well as being carbon conscience about of products and the manufacturing process, Low-E insulation will also reduce Life Cycle running costs in use. Placing less load on heating and cooling systems, means less energy consumed and less CO2 output. Current studies show that once the life cycle savings are taken into consideration Low-E Insulation has a Carbon Negative Footprint.
With older buildings in the UK accounting for 95% of Carbon emissions it is important for us that Low-E Insulation is just as easy to retrofit as it is it to install in a new build.





Recent Comments